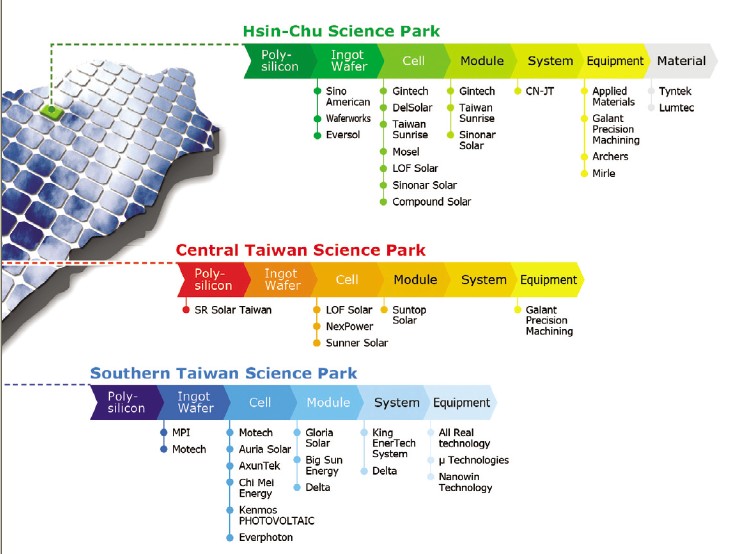
Figure 1. Taiwan solar cell clusters in science parks
By PIDA
As Taiwan’s PV industry has been pushing for rapid progress in recent years, the entire industry supply chain was established and the industry cluster was also strengthened. The annual capacity of the solar cell industry has made Taiwan one of the top five solar cell manufacturing countries in the world. Of all the PV suppliers in Taiwan, there’s a trend of suppliers gathering in the science parks to exploit the synergy and collaboration of the vertically integrated clusters, as shown in Figure1.
As for now, most PV companies gather in Hsin-Chu Science Park (HSP) and Southern Taiwan Science Park (STSP). As shown Figure 2, it can be seen from the figure that companies in these two science parks contribute more than 60% of the total production value in Taiwan. As to HSP, notable players include DelSolar Co., Ltd., E-Ton Solar, Gintech Energy Corporation, Motech Industrial Inc., Neo Solar Power Corp. (NSP) and more. The revenue of these companies amounted to near 40 billion NT dollars in 2009 and occupies more than 40% of the total production value of Taiwan, though presenting a 16% decrease from that in 2008.
In the Southern Taiwan Science Park, a complete PV industry supply chain, from upper stream material, midstream cell, to downstream module/system, is gradually taking shape as Motech pursues a vertical integration strategy and Delta steps into the module production and system installation field. The production value of STSP is estimated to be 16 billion NT dollars, about 18% of the total production value; besides, as Motech, Kenmos Photovoltaic, Tai-photovoltaic technology, Taiwan Polysilicon, MJC PROBE, Gloria Solar, NANO-WIN TECH, and Delta have their production bases firmly rooted in STSP. The STSP is aiming to become a significant PV industry cluster in the Southern Taiwan region.
In the Central Taiwan Science Park, NexPower Technology Corporation was founded by one of the worldwide leading IC foundry providers, UMC Group. Since 2005, NexPower sees itself as the pioneer in the silicon thin-film industry in Taiwan. Another thin-film player Sunner Solar Corporation was founded in June, 2007. In the first phase, Sunner Solar will employ a 25 MW a-Si PV module production line, and the second phase will involve the production of the latest thin-film product of amorphous and microcrystalline tandem. Furthermore, in the module field, Industrial Technology Research Institute of Taiwan (ITRI) works with Suntop Solar Energy to optimize the process technology for PV module. In addition, other companies distributed outside the science parks contributed 31.1 billion NT dollars to the total production value of Taiwan, or a 35% of share for 2009.
As for now, most Taiwan PV manufacturers in the science parks concentrate on the middle stream field. But when more companies are hurrying to raise their capacities in this sector, many have noticed the importance of material and silicon wafer and shifted to the upper stream sector. For example, SR Solar Taiwan, which is mainly invested by SRI (US), planned to use sodium reduction process to manufacture polysilicon. Led by thin-film makers NexPower Technology and Sunner Solar, and then followed by ITRI and Suntop Solar Energy, more PV companies are responding to CSP’s recruitment; therefore, in the future, CSP is looking to catch up with and even surpass the production values of HSP and STSP.
High Efficiency Race
There’s a trend observed from the HSP tenant enterprises that efficiency is now the first priority for manufacturing silicon-based solar cells. For example, DelSolar is expanding its R&D efforts from the solar cell manufacturing process to related issues and equipment both upstream and downstream. DelSolar partnered with upstream companies, Sino-American Silicon Products, Inc., and Green Energy Technology Inc. and the downstream company Tynsolar Corp. to deliver cell conversion efficiencies of 17.2% for mono-silicon solar cells and 16% for multi-silicon solar cells with a wafer thickness of 180μm. Up to now, the DelSolar R&D team has realized the efficiency to 18.7% and 17.3% on mono- and multi-Si cells, respectively. Gintech started to provide Douro, a polycrystalline silicon solar cell with a conversion efficiency of 16.6% in 2009. The new cell measures 156 x 156 mm, and the substrate is 180 to 200μm thick. Gintech is currently selling its cells in 42 categories with conversion efficiencies from 15 to 17%. In addition to the polycrystalline silicon cell, Gintech enhanced the conversion efficiency of its monocrystalline silicon solar cell to 17.1% or higher on average by improving the manufacturing process.
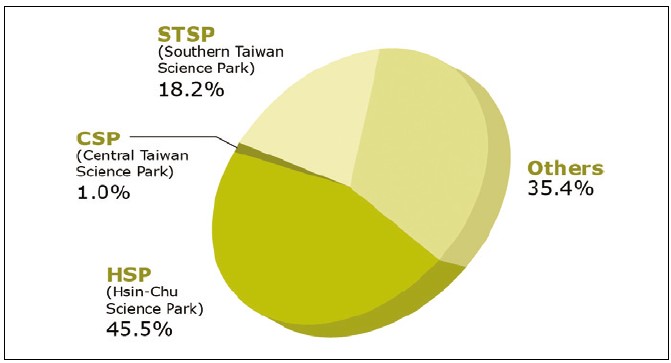
Figure 2. Taiwan PV production value breakdown
Color Solar Cell from Manufactures
Another interesting product is from LOF SOLAR, which has developed the first ever high efficiency color solar cell in the world. The company claimed that its conversion efficiency is 30% higher than the competitor’s products. Its C-Cell color solar cells are now available in green, purple, red, gray, etc. With LOF’s patented nano technology, the C-CellTM conversion efficiency can reach beyond 15% and has been confirmed by the Fraunhofer ISE (Institute for Solar Energy) in Germany. And their life time is comparable to the traditional blue solar cells, easily passing 25 years. In the past, the monochrome color of these cells inhibited its use in aesthetic design. As a response to the traditional monochrome solar cells, LOF’s colorized solar cells do not hamper conversion efficiency, and its design can be combined with the exterior hues of buildings and houses, to enhance color coordination.
Meanwhile, Gintech also announced in 2009 to provide green, purple, grey and silver color solar cells with transfer efficiency as high as 16%. The leading PV company Motech Solar is tapping into the color solar cell market as well. It provided sample with efficiency between 12% and 15%.
Taiwan’s PV Rush
In Taiwan, over the past few quarters, just about all the major players in the semiconductor industry have drawn up plans to rush into the solar industry with the type of precision technology and manufacturing techniques that can maximize production and efficiency given that both are based on silicon wafer. Among all, manufacturing giants demonstrate the most overwhelming ambition.
TSMC Expecting Revenue Growth by Entering Energy Industry
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC), the world’s largest contract chip maker by revenue, makes big progress after a string of moves to enter the industry.
Last June, former Chief Executive Officer Rick Tsai, who was appointed in 2005, was transferred to the company’s New Business Development Organization. Serving as president, Tsai will focus on the growth markets including solar and Light-emitting Diode (LED). TSMC hopes new businesses could add US$2 billion in revenue/year by 2018, which would put the company in a completely different valuation class.
Two months later, TSMC approved a budget of US$50 million for solar energy-related investments. Around the same time, according to a report in the local newspaper Commercial Times, the pure-play foundry bought a portion of the stake, approximately 11.2%, in Neo Solar Power, a Taiwan-based solar cell maker, through its venture capital affiliate VentureTech Alliance. Although, a source said in the story, the holdings are not high enough to warrant a disclosure to the watchdog Taiwan Stock Exchange (TSE), it underscores the company’s efforts to diversify into the solar market.
Since then, speculations about TSMC’s next acquisition of another solar cell manufacturer become rampant in the market. Those names that were alleged in talks with TSMC included Motech Industries, Taiwan’s largest solar cell manufacturer, E-Ton Solar Tech, the island’s second largest solar cell maker, and etc.
In December 2009, TSMC announced to purchase a 20% stake in Motech at a cost of approximately US$193 million. By becoming the single largest shareholder in Motech, TSMC entered the solar market fast. The company said the investment would allow it now to be better placed to evaluate its future solar strategy.
Most of analysts said it a good deal as Motech takes the lead in the industry and has a competitive edge. Also, although the new business would contribute to TSMC at less than 1% of its total revenues of NT$364 billion in 2010, it helps the company catch up the green energy trend.
It happens that there is a similar case. Last August, while TSMC was visiting several solar cell companies for potential alliance, United Microelectronics Corp, a major competitor to TSMC, created a business development center and venture capital fund called UMC New Business Investment Corp to invest in the solar and LED sectors.
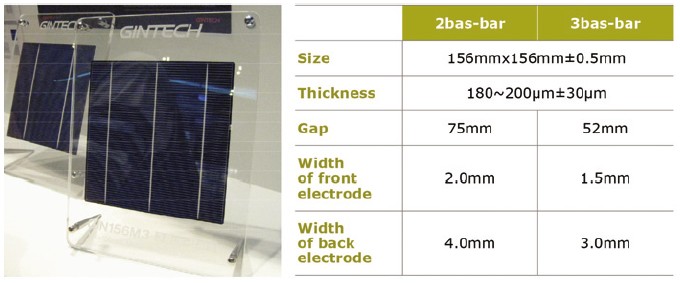
Figure 3. 6” high efficiency poly solar cell from Gintech
UMC Marching into China Solar Market
According to the other local newspaper Economic Daily News, UMC became the first foundry to step in planning to enter the mainland China as it applied to Shandong government to set up a handful of projects with regard to solar and LED. The total investment amount reached as high as US$300 million.
In the last two months of 2009, UMC set up several green investments in China, including a photovoltaic system company in Shandong Province through its Hong Kong-based affiliate with US$1 million, and the other two LED investments. UMC Chairman Stan Hung vowed to build the largest solar and LED manufacturing base within five years.
In fact, UMC has deployed the green energy industry, solar and LED in particular, without being noticed for a couple of years. In 2005, it established NexPower Technology Corp, a thin-film PV manufacturer in Taiwan, to make a study of product development, research and development, and manufacturing for the photovoltaic industry. Starting 2008, NexPower threw itself into volume production and expected to operate its plant at a rate of 12.5 MW per year. The company hopes to expand production volume gradually to reach an ultimate production goal of 100MW/year from that point.
AUO Established AET to Provide System
Integration Services
On the other hand, AU Optronics Corp, Taiwan’s biggest Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) panel maker who focuses on thin-film solar, planned its solar business as well. Last May, AUO created AUO Energy Taiwan Corp (AET), which will provide its customers with integrated technical supports in energy system. AET President Max Cheng hoped to do more by offering more extensive value-added services in the future such as installation of solar energy systems and other renewable energy sources for industrial facilities, company buildings and households. Currently, AET participates in relevant solar energy projects in Taiwan and around the world with its system providers.
Aside from spin-off decision, AUO’s board of directors approved a preliminary plan to subscribe new shares to be issued by M.Setek, a major polysilicon and monocrystal silicon wafer manufacturer in Japan. The investment cost AUO US$125 million, which was interpreted as an aggressive attempt to diversify into the green energy industry, but AUO said it will eventually purchase more than 50% of M. Setek shares in the future.
Moreover, AUO is allegedly considering purchasing 50MWp of solar cells from E-Ton in 2010. E-Ton President Allen Guo said both are indeed in talks with each other on future plan. He didn’t reveal more details but said that he expected to ink agreement for cooperation once the deal is done.
According to industry sources, E-Ton is a major buyer of M.Setek, whose 15% stake is owned by AUO, so AUO might be paving the way for a possible cooperation. The sources also commented that by securing part of E-Ton’s capacity, AUO will not only complete its supply chain by seize the opportunity to take the lead.
A Trend Worldwide
A similar trend is taking place in other countries in Asia, as well as in the U.S., making the competition more and more intensive. Earlier last year, semiconductor equipment maker Tokyo Electron Ltd. partnered with Sharp Corp. to work on new tools development for solar cell manufacturing. Its principal rival, Applied Materials, broke ground on a new US$60 million factory in Singapore.
National Semiconductor introduced its first solar product in last June; Intel Corp. announced to invest US$38 million into a German solar company; IBM Corp. gave itself into the business to team up with a Japanese company to develop new solar technologies; even Hewlett-Packard Co. recently licensed its transparent transistor technology to a Silicon Valley company who promises to make solar panels twice as efficient and half as expensive.
The Photonics Industry & Technology Development Association (PIDA) (http://www.pida.org.tw/) is a non-profit organization working with private enterprises and government agencies to increase the competitiveness of Taiwan’s optoelectronics industry.
For more information, please send your e-mails to pved@infothe.com.
ⓒ www.interpv.net All rights reserved
|